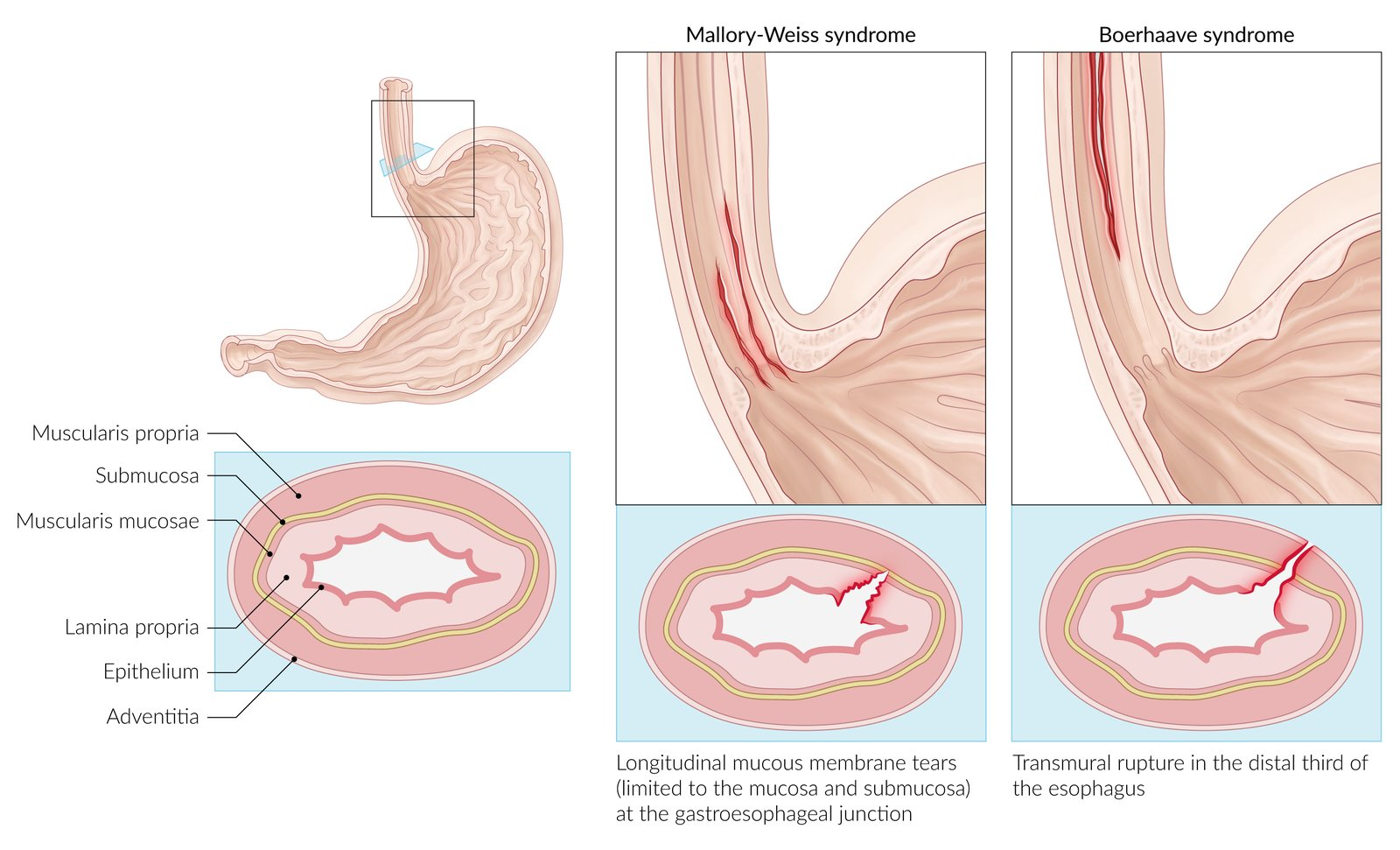
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
Epidemiology
- Sex: ♂ > ♀ (3:1)
Etiology
- Mechanism: a sudden and severe rise in the esophageal intraluminal pressure results in tearing of the esophageal mucous membrane, as well as the submucosal arteries and veins
- Precipitating factors
- Severe vomiting
- Predisposing conditions
- Alcohol use disorder
- Bulimia nervosa
- Hiatal hernia (higher pressure gradient)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- May be asymptomatic
- Epigastric or back pain
- Hematemesis
- typically follows a period of severe, bloodless vomiting
- Possible shock
Diagnostics
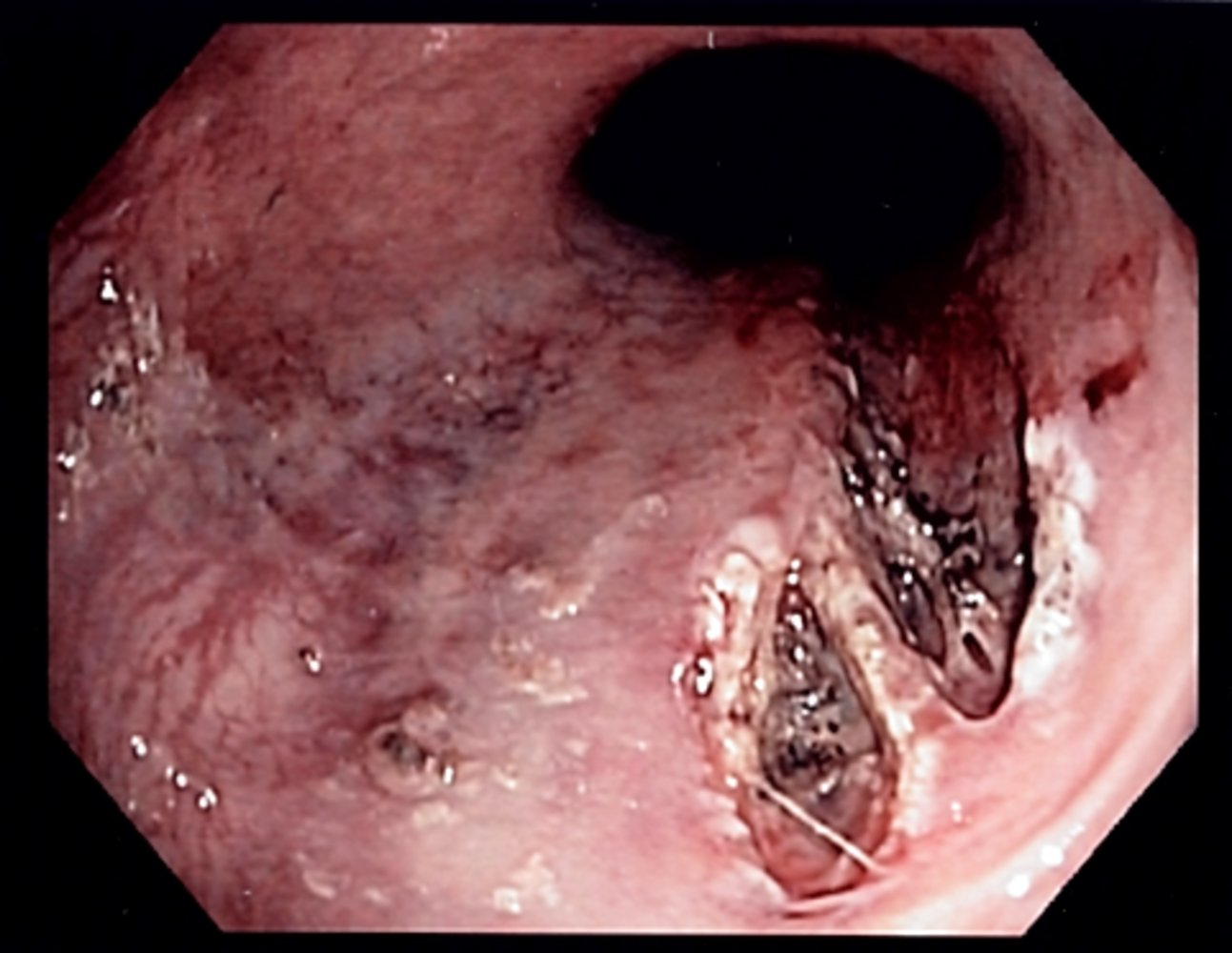
EGD
- Typical findings
- Often a single longitudinal tear (but multiple tears are possible) in the mucosa at the gastroesophageal junction or in the cardia of the stomach which are limited to the mucosa and submucosa
- A fibrin crust over the split, a clot, or active bleeding may be evident.
Differential diagnostics
| Characteristics of Gastroesophageal Mural Injury | Mallory-Weiss Syndrome | Boerhaave Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Forceful retching | Forceful retching |
| Mucosal tear | Transmural tear | |
| Submucosal venous or arterial plexus bleeding | Spillage of esophageal air/fluid into surrounding tissues | |
| Clinical Presentation | Epigastric/back pain | Chest/back/epigastric pain |
| Hematemesis (bright red or coffee-ground) | Crepitus, crunching sound (Hamman sign) | |
| Possible hypovolemia | Odynophagia, dyspnea, fever, sepsis | |
| Studies | Upper GI endoscopy confirms diagnosis (& can treat persistent bleeding) | Chest x-ray: pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pleural effusion |
| Esophagography or CT scan with water-soluble contrast confirms diagnosis | ||
| Management | Acid suppression | Acid suppression, antibiotics, NPO |
| Most heal spontaneously | Emergency surgical consultation |